Transferring large files over the Internet has always been a challenging task, especially when it comes to uploading files several gigabytes or even hundreds of gigabytes to cloud servers or downloading them from servers. Success depends on a bit of luck. The reasons for this difficulty are roughly as follows:
- The Internet speed is unstable and the transmission process is so unstable that it can be interrupted
- Commonly used transmission protocols, such as http and ftp, have weak recovery capabilities when transmission is interrupted
- The time span for large file transmission is long, and the probability of no problems occurring throughout the entire transmission cycle is relatively low
OnTheSSH supports file splitting transfer and is a solution to the problem of large file transfer. The following figure shows the working principle:
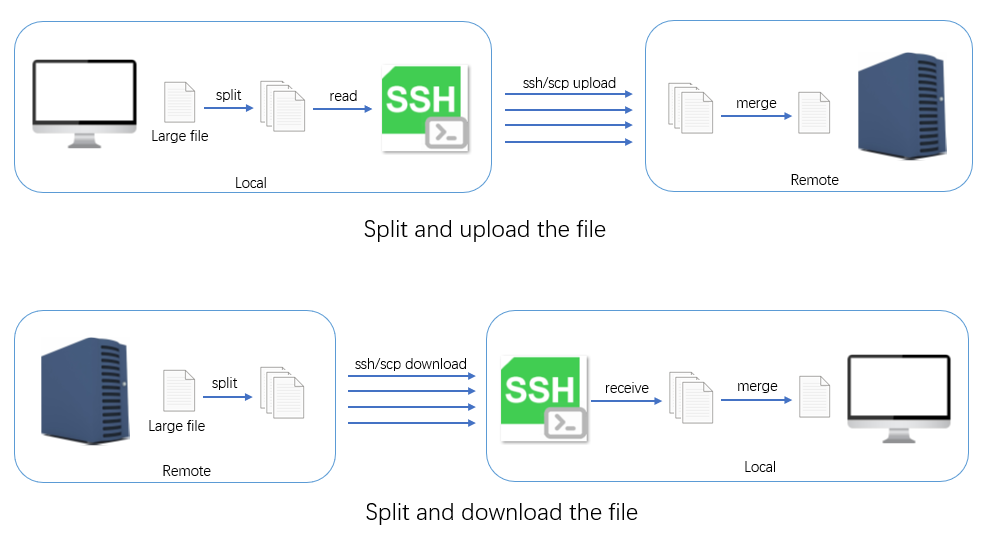
Before transmission, the large file is first split into many block files at the source end, then these block files are transmitted, and finally these block files are merged at the destination end. OnTheSSH manages and controls the following processes during transmission:
- Obtain the size of the source file, set the size of the block file, and split the source file.
- Block files are concurrently transmitted via the ssh/scp protocol. During the transmission process, the transmission status of each block file is monitored. If the transmission of any block file fails or times out, it will trigger the retransmission of this block file until it is completely transmitted to the destination end.
- When all the block files have been transferred, merge the block files.
How to use split transmission
Click on the remote host you want to transfer to in the left sidebar (here it is Ubuntu), and then click the “Host Window” button on the right. The interface will display as follows:
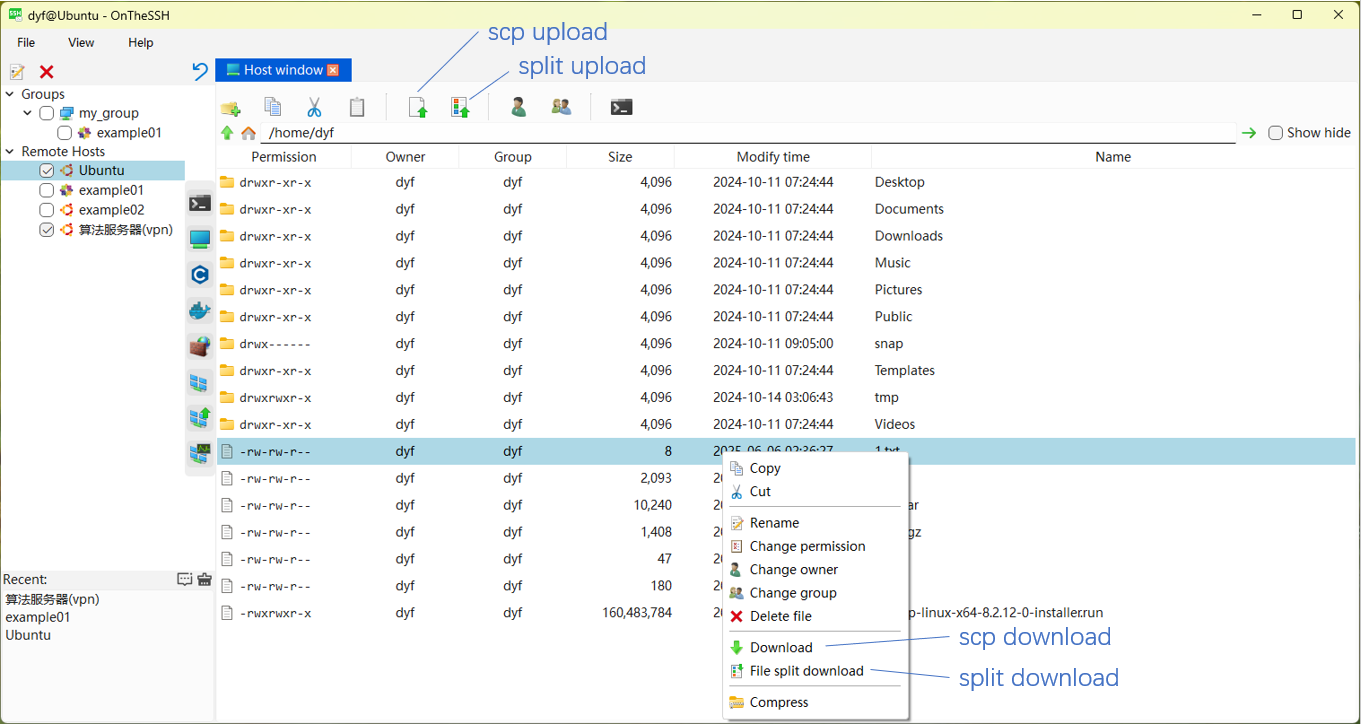
In the Host window TAB, click the Split Upload button at the top to split and transfer local files to the current directory. Right-click on a file in the list, and in the pop-up menu, click the Split Download menu to split and transfer this file to your local device.
Click the “Split Upload” button at the top, and a pop-up window will appear to configure the split file (the configuration for split download is similar and will not be elaborated here) :
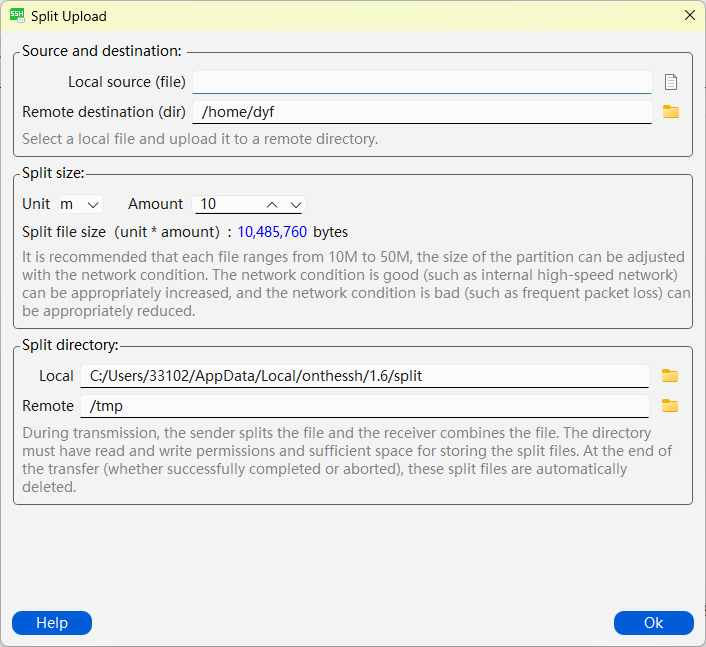
In the Source and Destination sections, select the local file you want to upload and the directory where you will remotely receive this file. In the split Size column, define the unit and quantity of the split blocks, which determine the size of the split block file (defined here as 10M). In the split directory column, set the storage directory for the local split block and the receiving directory for the remote split block.
The following is a screenshot of the interface during the transmission process:
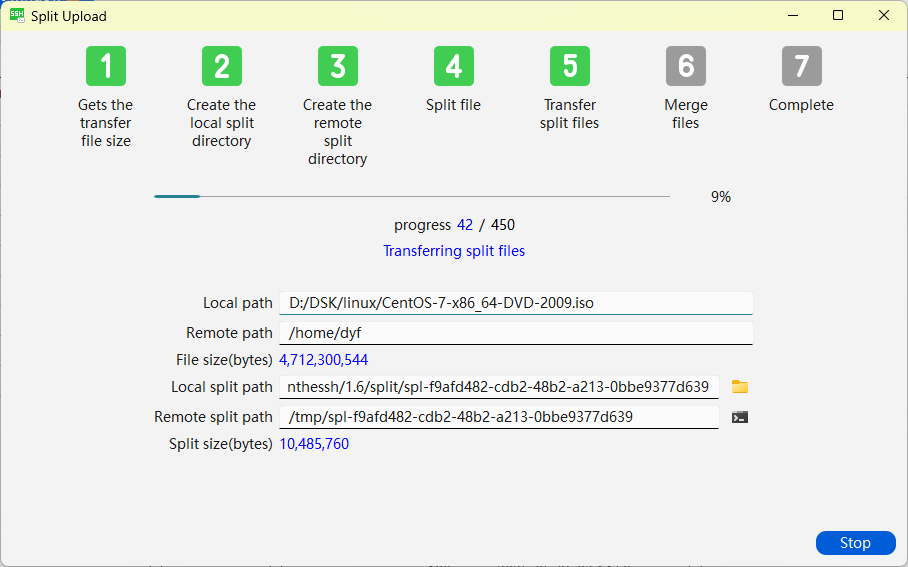
As can be seen from the above figure, the transferred file is the CentOS installation disc ISO, approximately 4.7G in size, uploaded to the /home/dyf directory. The size of the split block file is 10M, and a total of 450 block files have been split. Currently, 42 block files have been transferred. The split transmission workflow has seven steps:
- Obtain the size of the source file
- Create a directory locally for storing split block files
- Create a directory for receiving block files at the remote end
- Split the file locally (split the file remotely when downloading)
- Transfer all block files. The transmission is carried out concurrently in multiple threads, with a maximum of five block files being transmitted simultaneously. If a block file fails to be transmitted or times out, it will be retransmitted.
- After the transmission is completed, merge the files at the destination end
- Completed. Automatically delete all local and remote block files during the transmission process
Note
When the transmission is completed normally or manually stopped, the directories where the local and remote temporary storage of the partitioned block files will be automatically deleted. However, in abnormal situations, such as sudden power outages or network disruptions, the remote partition block files cannot be deleted in time and will occupy disk space. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly check the disk space usage to avoid disk overflow.
The disk space for storing partition blocks locally and remotely should have an appropriate remaining disk capacity. The default locations for local and remote storage of split-block files are set in the menu “File” – “Preferences” :
Other online documents:
