Port forwarding is a feature of the SSH protocol. It allows you to specify a port on one host and use an SSH connection as a proxy to forward the network connection on that port to a port on another host.
Port forwarding is typically used for two purposes:
- Port forwarding is more secure in the network because the transmission takes place through the SSH encrypted channel.
- The internal service port (blocked by the firewall) can be opened to users through the SSH channel.
OnTheSSH offers a graphical interface for port forwarding, which is simple to use and less prone to errors. Let’s first look at an example of a simple scenario:
Simple scene
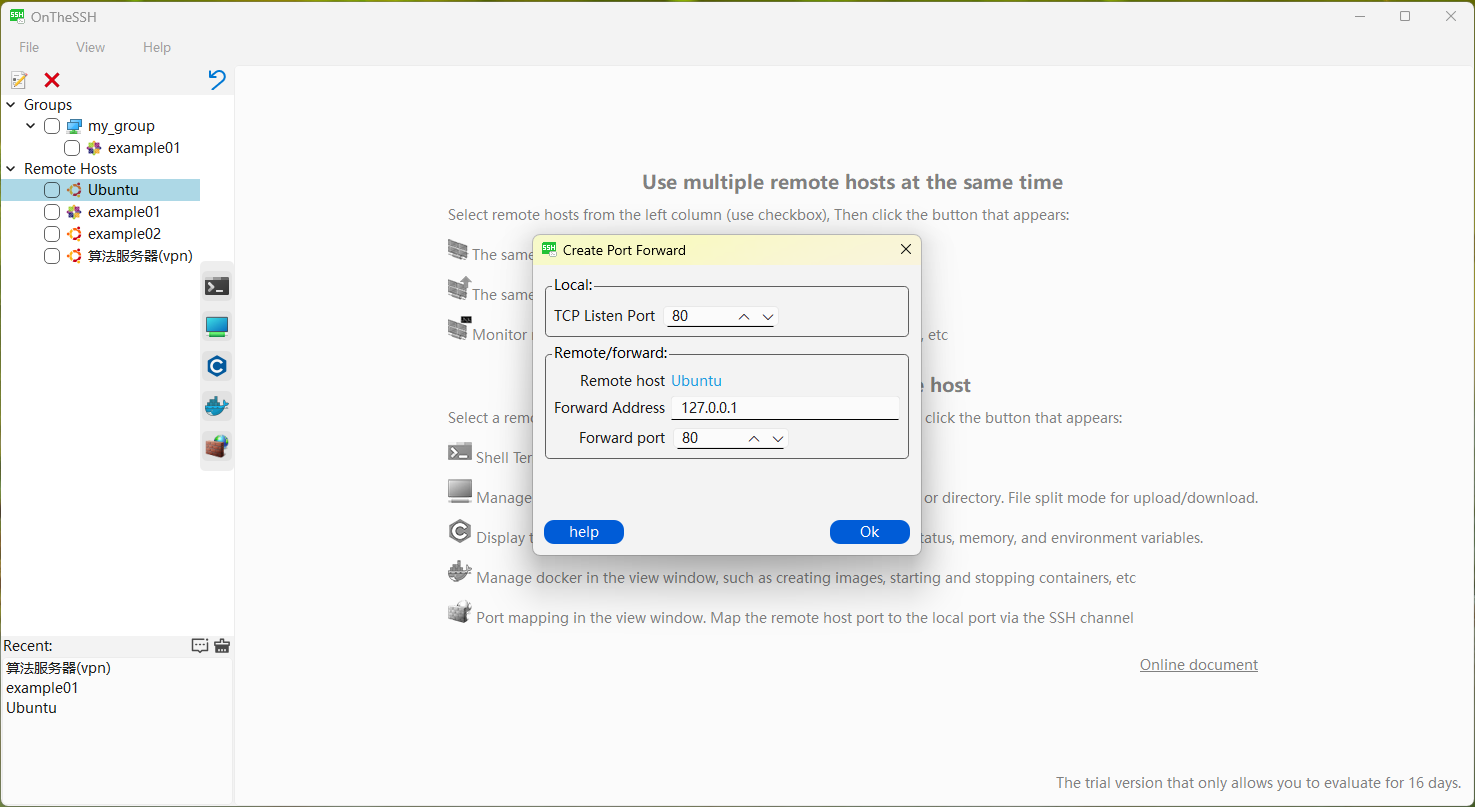
Click on a remote host (this is Ubuntu) in the left sidebar with the mouse, and then click the “Port Forwarding” button on the right (the icon looks like a firewall). A dialog box will pop up as shown in the above picture. The local TCP listens on port 80, and the remote forwarding address is 127.0.0.1 on port 80. Clicking OK will create an SSH channel that forwards local port 80 to remote port 80, as shown in the following figure:
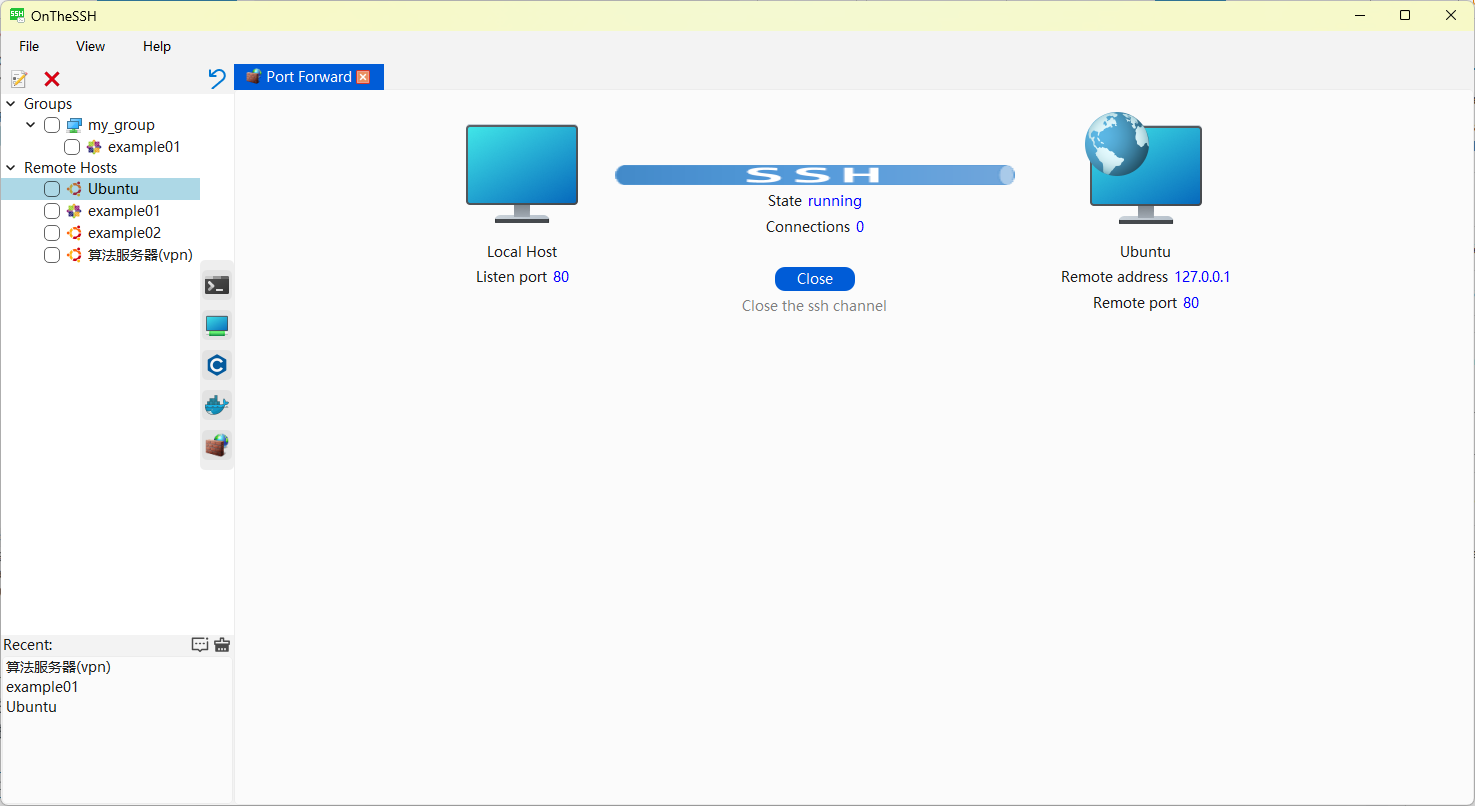
Here, it shows that a port forwarding channel has been created. The status “running” indicates that the channel is running (port forwarding has been created successfully), and the number of connections 0 indicates that there are no socket connections in use yet.

This example is a typical usage scenario where typing http://localhost:80 in the localhost browser will access the http service content at the remote end.
Complex scenes
Port forwarding can also create more complex scenarios. Note that in this example, the port to be forwarded is not on the remote host of the SSH channel.
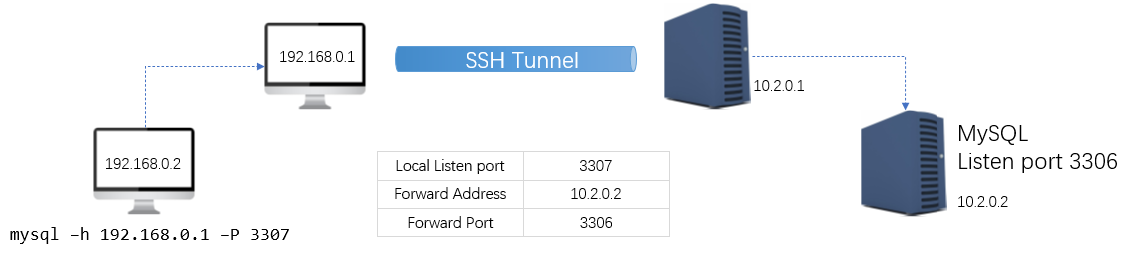
The SSH channel is established between the local 192.168.0.1 and the remote 10.2.0.1, but the Mysql service to be accessed is on the remote 10.2.0.2. Originally, the Mysql service was inaccessible on the 192 network segment. There might be a firewall blocking the connection between the two network segments. However, through port forwarding, the 3306 port of the Mysql service can be mapped to the 3307 port of the local host 192.168.0.1, allowing the Mysql service to be accessed locally.
Pay attention to the setting of the remote forwarding address. It is the address for accessing the Mysql host from the 10.2.0.1 host. In the previous simple scenario, the forwarding address was configured as 127.0.0.1, which was also configured from the perspective of the remote host of the SSH channel. 127.0.0.1 is itself.
Other online documents:
